Announcement
- Proposal submission for AUC-79 will start from 15 September 2025 and will end at 5:30 PM on 15 October 2025.
- Director Interview on DD Morning Show | SEMICON India 2025
- Workshop on Indian National Gamma Array: New results and Future Perspectives 563.55 KB
- Registration open for Workshop on Atomic and Molecular Physics – 2025.
- The last date for Research Associate (RA) form (Advertisement No 03/2025) submission has been extended to 31 August 2025 267.12 KB
- The School on Geochronology Techniques (SGT) will be held at IUAC from September 29, 2025, to October 04, 2025. 449.12 KB
- Advertisement no. 04/2025 for one year Apprenticeship Training
- IUAC invites the applications for the position of Research Associates (RA). Advertisement No 03/2025
- Advertisement No: - 02/2025:IUAC invites applications for the position of JRF
- List of approved proposals: AUC-78 342.63 KB
- PhD (Physics) Programme course schedule monsoon semester, August 2025 - December 2025 200.09 KB
- School-cum-Workshop on “Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation” , 24-26 September 2025
About IUAC
Inter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) was set-up by the University Grants Commission as the first Inter-University Centre (IUC) called Nuclear Science Centre after due approval of the Planning Commission and the Prime Minister in October, 1984. Its construction started in December, 1986 and completed in time on December 19, 1990.
The basic objective of Inter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) is to provide front ranking accelerator based research facilities to create possibilities for internationally competitive research within the university system. The Centre has been playing a very special role of a research institute within the University system where the scientific and...
Read MoreFrom
Director's
Desk

Prof.
Avinash Chandra Pandey
Director
With more than three decades of experience in the field of accelerator driven science, Inter University Accelerator Centre (formerly -Nuclear Science Centre) has earned its reputation of excellence in the Indian academia.....
Read MoreAccelerators
- Pelletron
- Superconducting Linear Accelerator
- Pelletron Accelerator RBS-AMS Systems
- Accelerator Mass Spectrometry
- Negative Ion Beam Facilities
- Positive Ion Beam Facilities
- Tabletop Ion Accelerators
- High Current Injector
- Free Electron Laser

Accelerator machine installed inside the accelerator tank as shown in the picture. High voltage upto 15 million volts is generated in the centre portion known as terminal. The Pelletron accelerator can be operated upto 15 MV of terminal potential and can produce dc as well as pulsed beam of a variety of elements. The pelletron has been operational since July 1991. The Pelletron has unique features like compressed geometry accelerator tubes for higher terminal voltage, offset and matching quadruples for charge state selection inside high voltage terminal and elaborate pulsing system in the pre-accelerating region consisting of a beam chopper, a traveling wave deflector, a light ion buncher (for ions of 1- 80 AMU) and a heavy ion buncher(for ions of >80 AMU).
Read More
The accelerating structure for the superconducting linac booster for the 15 UD Pelletron at IUAC is a Niobium Quarter Wave Resonator, designed and fabricated as a joint collaboration between IUAC and ANL, USA. Initial resonators required for the first linac module were fabricated at ANL. For fabrication of resonators required for future modules a Superconducting Resonator Fabrication Facility has been set up at IUAC. Three quarter wave resonator (QWR) have been fabricated and fifteen more resonators for the second and third linac modules are in advanced stage of completion.
Read More
Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS) facility with 1.7 Million Volt Pelletron accelerator has been installed at IUAC. The facility is equipped with :
- Alphatross ion source for producing negatively charged He and H ions.
- 1.7MV 5SDH-2 Pelletron accelerator
- Charles Evans and Associate make 4 − axis goniometer (model name RBS-400)

Accelerator Mass Spectrometry with 15UD Pelletron at IUAC is first AMS facility in India for the detection of 10Be and 26Al . This facility is now open for users to carry out 10Be and 26Al measurement work.
AMS is mass spectrometry using Accelerator. AMS is used to measure the very low concentration of trace elements. These trace elements generally are long lived radioisotopes and some times stable isotopes. Long lived radioisotopes serve as tracers and chronometers in many branches of science e.g. Geology, Archeology, Hydrology, Environmental Science, Biomedicine, Cosmo-Chemistry and Nuclear Physics etc. AMS is also used to determine stable isotopes at ultra trace levels in semiconductors, geological samples and other materials.
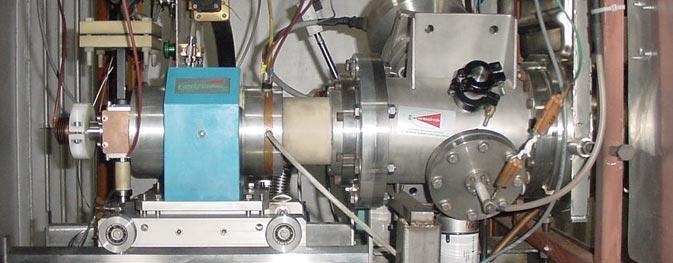
Ion implanter accelerator facility at Inter University Accelerator Centre provides varieties of highly stable, collimated negative and singly charged ion beams with variable low energies, 30 to 200KeV and current intensities, few nA to few μA. This makes the facility an excellent tool to do research in material science through ion-solid interaction in nuclear energy loss regime such as material synthesis, device fabrication and material modifications. The accelerator equipment essentially consists of an ion source, an accelerating column, mass analyzer and a target chamber, where the ions impinge on a target. The design and development of the facility has been done indigenously with several beam line components developed in-house at IUAC such as high voltage platforms, electrostatic Quadrupole triplets lens, electrostatic Quadrupole steerers and high vacuum experimental chambers.
Read More
The ninety degree beamline is used for material science experiments (including implantation, surface modification, sputtering etc) in a dedicated chamber provided with a multiple sample holder that can be either heated (for high temperature implantation, for example) or cooled to liquid nitrogen temperatures. In addition online electrical conductivity measurements can be done.
Read More
To inculcate the interest of young faculties & students towards the Physical Sciences in education & research we have in-house developed 60 kV Tabletop Ion Accelerator and 30 kV Tabletop Ion Accelerator for Physics students & faculty at the University/College level.
Read More
The High Current Injector (HCI) project was envisaged to overcome the low current limitation of the Pelletron Accelerator and to provide varieties of ion species like Nobel gases etc. which are not possible with existing Pelletron Accelerator. The high current from HCI will not only reduce the number of shifts needed for carrying out the experiments but will also enable usres to carry out very low cross section nuclear reactions studies which are not possible using beams from Pelletron due to its low current limitations. The HCI would use a Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ), Drift Tube Linac (DTL) and low beta superconducting cavities to accelerate heavy ions having A/q ≤ 6, from the high temperature superconducting electron cyclotron resonance ion source (HTS-ECRIS called PKDELIS) to the existing superconducting linear accelerator (SC LINAC). The DTL has been designed to accelerate ions from 180 keV/u to 1.8 MeV/u, using six Interdigital-H (IH) type RF resonators operating at 97 MHz. The required output energy of the DTL is decided by the minimum input velocity (beta = 0.06) required for the existing superconducting LINAC. IH type resonators are the preferred choice for multiple gap DTL applications due to their high shunt impedance. Acceleration from 180 keV/u to 1.8 MeV/u would be done by six independently phased IH type RF cavities.
Read More
A compact, pre-bunched Free Electron Laser facility named as Delhi Light Source (DLS) is presently under construction at Inter University Accelerator Center (IUAC). The accelerator facility, the complete beam line and the experimental facilities are being accommodated in a class 10000 clean room. A low emittance pulsed electron beam will be produced by a photocathode based normal conducting RF gun (figure 1) operating at 2860 MHz and will be injected into a compact undulator to produce THz radiation. The Klystron and Modulator systems are being commissioned at IUAC (Figure 2). Beam optics calculations were performed with the GPT and GICOSY codes. Another code, developed in-house, based on Lienard-Wiechert potential formulation, is used to calculate the parameters of the THz radiation emitted from the wiggling electrons inside the undulator. The design of the laser system has been completed and the system is being developed in collaboration with KEK, Japan.
Read MoreResearch Areas
Outreach Program
This program is conducted in two semesters The Spring Semester (January - May) and Fall Semester (August - December)...
Read MoreInter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) conducts M. Sc. Orientation Programme to encourage interested students to supplement their knowledge and to motivate them to continue their career in science. This programme has been envisaged to provide hands-on training in fields associated with accelerator based research to selected M. Sc. students by way of short projects...
Read MoreA few B.Sc (Physics) students who are in their 2nd /3rd year and are seriously considering pursuing higher studies in Physics are invited to IUAC for about 4 weeks during May-June every year for the SUMMER PROJECT training in this Centre...
Read More



































